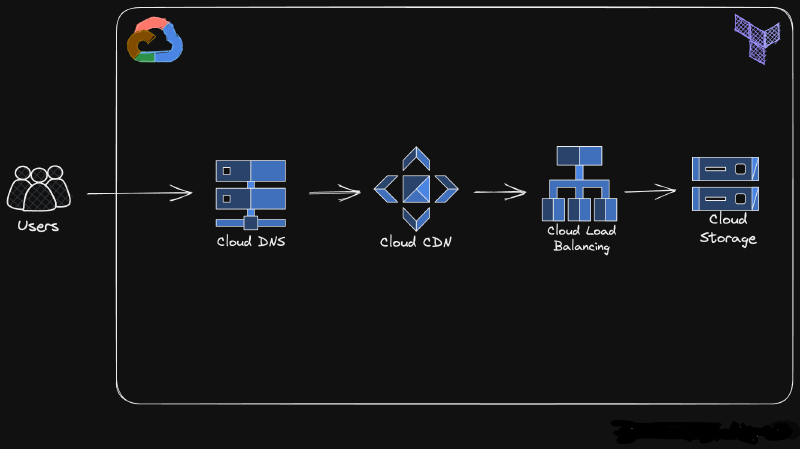
Architecture 🏗
Hey!👋 I am Dominik and this project is a Terraform configuration that creates a static website on Google Cloud Platform.☁ The website is my personal portfolio and is hosted on a Cloud Storage bucket. The website is served using an HTTPS load balancer, which provides SSL termination. This ensures that all traffic to the website is secure and encrypted. The website is accessible at www.domssocial.co.uk.
The project also creates a DNS zone for the website, which is used to route traffic to the load balancer. And the Cloud CDN is used to cache the website content and improve performance.
NOTE: This website is currently not accessible as the infrastructure has been scaled down to minimize costs.
❔Why did I do this? I wanted to create a simple, cost-effective way to host a static website on Google Cloud Platform. I also wanted to learn how to use Terraform to create infrastructure on GCP.
🤷♂️So what is a static website? A static website is a website that is made up of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. These files are served directly to the user’s web browser, without any server-side processing. This makes static websites fast and cost-effective to host.
☝Pre-requisites:
- A Google Cloud Platform account and a project
- The Terraform CLI
- A text editor like Visual Studio Code
1.🌀To get started, clone the project repository to your local machine and change directory to the project directory
| |
| |
2. Set up your Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Before you start configuring the project, you will need to set up your GCP account and create a project.
- Create a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) account
- Create a new project
- Create a service account for the project
- DNS zone for the project
- You will also need to register a domain name and configure it to use Google Cloud DNS - I used https://domains.squarespace.com/ to register my domain, however you can use any domain registrar.
- In GCP you will need to enable some API services like IAM Service Account Credentials API, Cloud DNS API…etc
3. Initialize the Terraform project
| |
4.Configuring the Project💻
I created 3 Terraform .tf files to configure the project:
main.tf- This file contains the main configuration for the project, including the Cloud Storage bucket, the IAM policy binding, the HTTP load balancer, and the Cloud CDN.variables.tf- This file contains the input variables for the project, including the project ID, the bucket name, and the index page.provider.tf- This file contains the provider configuration for Google Cloud Platform.
5. Download and add your JSON key file to the project
The service account key file is used to authenticate Terraform to your GCP account. You can create a service account and download the key file by following the instructions in the GCP documentation.
6. Creating the Static Website
Once you have configured the project, you can upload the Terraform configuration to Google Cloud Platform by running the following command:
| |
To check the changes that will be made to your infrastructure.
| |
When prompted, review the changes and type yes to confirm that you want to apply the changes.
Terraform will then create the following resources:
- A Cloud Storage bucket
- An IAM policy binding that grants the storage.objectViewer role to the allUsers group
- Cloud CDN for the bucket
- SSL certificate for the domain
- An HTTPS load balancer
7. Testing the Static Website👏
Once the static website has been created, you can test it by visiting the following URL: <www.domssocial.co.uk>
How it works🧮
When a user visits the website, the following steps occur
1. Cloud DNS: The user enters your domain name in their browser. Cloud DNS translates the domain name to the IP address of the Cloud CDN edge location closest to the user.
2.Cloud CDN Caching: The user's browser connects to the nearest Cloud CDN edge location. Cloud CDN checks its cache for the requested content (static files like images, HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
3.Cache Hit: If the content is already cached at the edge location, Cloud CDN serves the content directly to the user's browser, resulting in faster delivery due to reduced latency.
4.Load Balancer: If Cloud CDN doesn't have the requested content cached, it forwards the request to the Load Balancer.
5.The Load Balancer distributes the request traffic across your backends, which are the Cloud Storage buckets that host your website content.
The Frontend design of the website
The frontend of the website is a HTML, CSS and JS files. I downloaded the template from https://html5up.net/, and modified it to suit my needs.
Skills gained📚
1. How to use Terraform to create infrastructure on Google Cloud Platform
2. How to create a static website on Google Cloud Platform
3. How to use Cloud Storage, Cloud CDN, and an HTTPS load balancer to host a static website
4. How to use and create Cloud DNS zones
5. How to use a service account key file to authenticate Terraform to Google Cloud Platform
6. How to create a SSL certificate for a domain
7. Gained some experience with HTML, CSS and JS